Repairs and maintenance benefit from the develoopment of the vehicle fleet
Vehicle maintenance is mainly driven by a vehicle fleet that is still growing
*Sources: AAA Data – Vehicles on the road in France in 2024
The average age of vehicles has continued to rise, reaching 11.9 years in 2024(1). The continuing increase in the price of new vehicles, coupled with the integration of new, costly technologies (GSR2-2024 standard for driving aids, electrification, connectivity and digitalization), is prompting motorists to keep their vehicles for longer, resulting in a lower turnover rate each year.
The total lifespan of a car is now 19.7 years(2): the fleet needs more maintenance operations throughout its life. Roadworthiness testing has adapted to this reality. Greater precision in measuring pollution from diesel vehicles (smoke opacity testing, 2019) means that diesel engines, which still accounted for the majority of the fleet on the road in 2023, need more maintenance.
1 Source : AAA Data | 2 Source : Ademe

Electronic maintenance
becoming more widespread and generating new needs.
The automotive repair lies at the point of convergence of three essential transformations which are
affecting all the sector’s professionals:
- ELECTRONIC MAINTENANCE
- ELECTRIFICATION
- DIGITALISATION & CONNECTIVITY
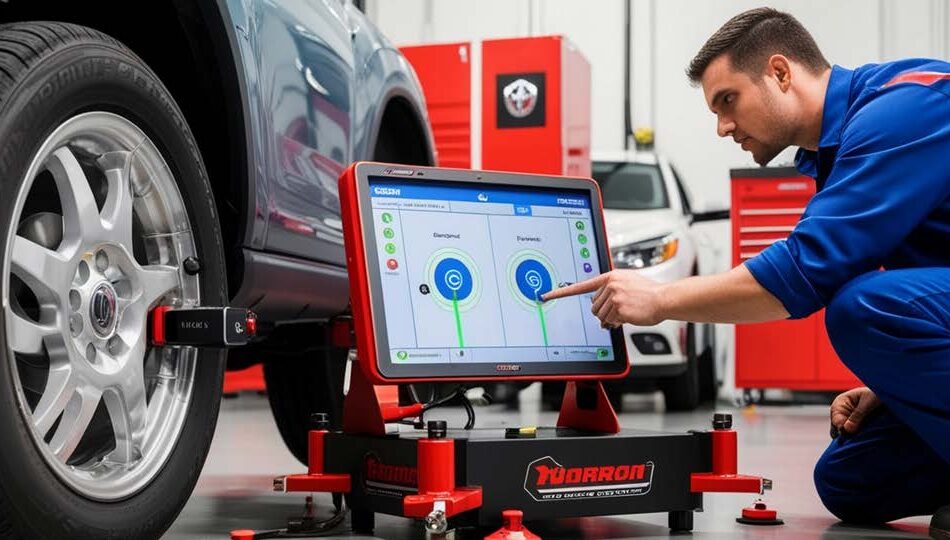
Electronic maintenance is the systematic use of diagnostic tools connected to vehicle control units. According to Gipa France, in 2023, independent repair shops used a diagnostic tool for 63% of workshop visits. The new generations of diagnostic tools can communicate using the computer protocol adopted by all manufacturers (SAE J2534). The use of dedicated
vehicle connexion interfaces (VCIs) allows any repairer to use a ‘pass-thru’ to access manufacturers’ data servers (subject to subscription) and download updates or computer maintenance codes for the ECUs in the most recent vehicles (remote coding).
The repair industry will have to spend a lot of time training to benefit from these new functions. However, given the wide variety of systems and interfaces on vehicle manufacturers’ repair and maintenance sites, a new standard is emerging, with maintenance delegated to platforms specialising in remote control and diagnosis (including downloading of updates and remote coding).
This shift, which is still largely undetected by the automotive repair industry, is fundamental and will be one of the key themes at EQUIP AUTO Paris 2025.
In 2024 SERMI removes another obstacle for all-make aftermarket players
The 2024 implementation of SERMI, the new security certificate for maintenance operations, led to strong demand for information on the part of repair professionals in manufacturer networks and independent outfits alike.
Thanks to SERMI, the release of vehicle security data to all-make aftermarket operators (immobiliser functions, coding of on-board access keys) will remove a new barrier to competition between automotive maintenance operators.
Electrification
is the gradual entry of vehicles with electric components in the fleet.
These range from the simple starter-alternator (launched on the Citroën C3 by Valeo in 2003) to the various forms of hybridisation:
• The 48-volt, which has become widespread;
• The so-called mild-hybrid traction assistance engine, located between the powertrain (engine-clutch-gearbox) and the transmission;
• The full-hybrid (such as the Renault E-Tech or Toyota HEV);
• The plug-in hybrid, which adds power electronics components;
• The electric vehicle with a 100% electric traction battery.
Throughout the transition phase between internal combustion engines and the switch to electric power for new vehicles (on 1 January 2036 in the European Union), repair and bodywork garages must gradually adapt to new diagnostic and maintenance techniques.
At EQUIP AUTO, workshop equipment manufacturers will be exhibiting tools that meet the new workshop standards for electric vehicles (tools, protective equipment, adapted or specific lifts for vehicles with voltages in excess of 60 volts).
Digitalisation & connectivity
are the latest big chapter in the evolution of the car repair sector.
Digitalisation means digitising maintenance data, which will facilitate remote repairs and the real-time consultation of updated repair data.
It also includes online workshop planning (on all-make repair websites or repair shop chains), allowing customers to book appointments remotely, as well as digital customer relations. Finally, there is e-learning. Connectivity, meanwhile, will enable the workshop to gradually become part of an ecosystem that connects smoothly with its customers, suppliers (including parts and equipment distributors), vehicle manufacturers and the world of service providers (e.g. insurers) or training providers, without losing time or information.

Repair and Maintenance
1.39 MoDownload